MLA Format Explained: A Complete Guide for Students
MLA Format Explained: A Complete Guide for Students
Step-by-step MLA formatting for title page, in-text citations, and Works Cited page (with templates)
If you’ve ever written a research paper or essay for school, chances are you’ve heard of MLA format. Short for Modern Language Association, this style is one of the most widely used formats for academic writing — especially in the humanities.
1. What Is MLA Format?
MLA format is a standardized way to present academic writing so readers can easily follow your ideas and verify your sources. The MLA Handbook outlines the latest rules on paper layout, citations, and referencing. See the official resource at the Modern Language Association website.
The three main parts you’ll need to master are:
- General paper formatting (font, spacing, margins, etc.)
- In-text citations (parenthetical citations in the body)
- Works Cited page (full list of sources at the end)
2. MLA General Formatting Rules
Start by setting up your document correctly.
- Font: Times New Roman 12 pt (or another easily readable font)
- Spacing: Double-spaced throughout (including the Works Cited page)
- Margins: 1 inch on all sides
- Indentation: First line of each paragraph indented 0.5 inch
- Header: Your last name and page number in the top-right corner
- Alignment: Left-aligned (not justified)
Quick MLA Template for a Standard Essay Page
Thuc Nguyen
Professor Smith
English 101
10 October 2025
The Impact of Digital Media on Reading Habits
Over the past decade, the way people read and consume information has changed dramatically...
Note: The title is centered — no bold, underline, or italics.
3. MLA Title Page Format (When Required)
MLA papers typically do not require a separate title page unless your instructor asks for one. If requested, follow this structure:
Your Name
Instructor’s Name
Course Name or Code
Date (Day Month Year)
Centered halfway down the page:
Paper Title (Title Case, No Bold or Underline)
Bottom-right corner: Last Name + Page Number
Example:
Emma Carter
Professor Johnson
English Literature 202
12 May 2025
Analyzing the Role of Nature in Romantic Poetry
Carter 1
4. MLA In-Text Citations (Parenthetical Citations)
When you quote, summarize, or paraphrase a source, include an in-text citation. The typical format is (Author’s Last Name Page Number) — no comma.
Examples:
- Direct quote: “Reading is essential for those who seek to rise above the ordinary” (Mortimer 87).
- Paraphrase: Mortimer argues that reading deeply helps individuals improve their critical thinking (87).
If there’s no author, use a shortened title: ("Digital Reading Habits" 5). If there’s no page number (e.g., a website), include only the author: (Smith).
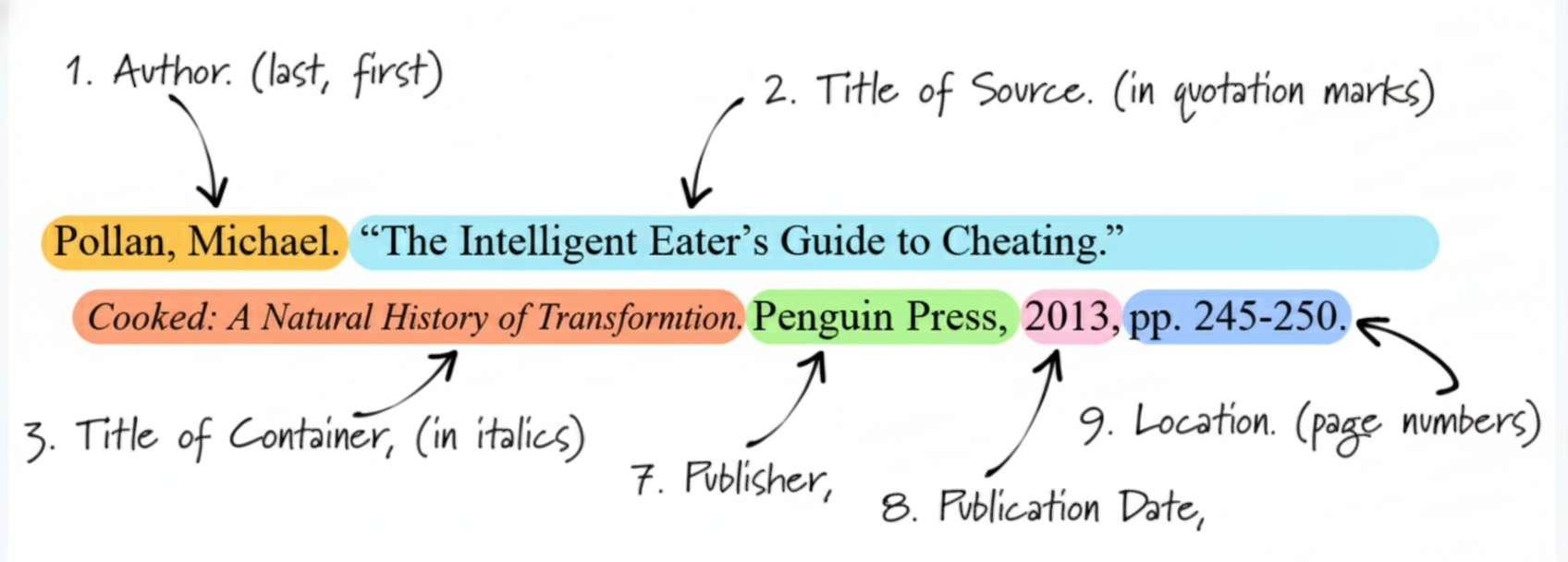
5. How to Format the Works Cited Page
The Works Cited page lists all sources mentioned in the essay and appears on a new page at the end.
- Title the page Works Cited, centered at the top.
- Alphabetize entries by author’s last name.
- Use hanging indentation for each entry.
- Double-space all lines.
Works Cited Templates
Book:
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year.
Journal Article:
Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, vol. #, no. #, Year, pp. xx–xx.
Website:
Last Name, First Name (if available). “Title of Webpage.” Website Name, Publisher (if different), Publication date, URL.
Example entries:
Orwell, George. 1984. Harvill Secker, 1949.
Smith, Laura. “Reading in the Digital Age.” Journal of Literacy Studies, vol. 12, no. 3, 2022, pp. 45–63.
Johnson, Mary. “How Reading Habits Have Changed in the 21st Century.” The Reading Hub, 5 Mar. 2024, www.thereadinghub.com/reading-habits.
6. MLA Citation Generators: Helpful Tools
Formatting citations manually takes time. These tools generate MLA citations quickly — but always double-check the output:
7. Sample MLA Paper Structure
Page 1: Heading + Body (header with last name & page number; centered title; essay starts).
Page 2+: Continue text with header on each page (include in-text citations as needed).
Final Page: Works Cited (new page, alphabetized entries, hanging indents).
8. Common MLA Formatting Mistakes (and How to Avoid Them)
- Forgetting the hanging indent.
- Incorrect header placement (last name + page number).
- Using bold/underline/italics for the title (keep title plain text and centered).
- Missing access dates on web sources when your instructor requests them.
- Mixing citation styles — stay consistent with MLA.
9. Final Tips for MLA Success
Check if your instructor has specific preferences, consult the MLA Handbook for unusual cases, proofread your Works Cited, and keep formatting consistent throughout.
Quick MLA Checklist
- Is my paper double-spaced with 1-inch margins?
- Does every in-text citation match a Works Cited entry?
- Are titles italicized and punctuated correctly?
- Is the Works Cited page alphabetized and properly indented?
- Does the header include my last name and page number?